
SMTP Settings
What is SMTP?
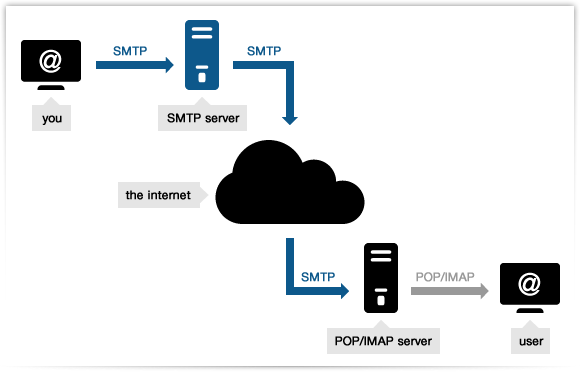
SMTP or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is an application that is used to send, receive, and relay outgoing emails between senders and receivers. When an email is sent, it’s transferred over the internet from one server to another using SMTP.
In laymen language, SMTP is simple decorum that is followed by emails for transmission through out the internet. In more plain terms, SMTP can be considered as a post office where sender deposits their email and it delivers to the receiver’s local post office i.e. another SMTP server.
Fun Fact – SMTP is able to transfer only text, it can’t handle fonts, graphics, attachments etc. That’s why you call it SIMPLE mail transfer protocol
You use MIME or Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions to send non-text content like multimedia. In the transformed format, SMTP is cajoled into transferring the data.
Advantages of SMTP
- All you have to do is use your credentials and it will work.
- In case of failure, the message will include an explanation about why email failed to be delivered.
- It is extremely easy to start using mail for your transactional emails. All you have to do is exchange ceremonial and you are set to go. Unlike with API, where coding is required.
Limitations of SMTP
- Some firewalls can block port commonly used with SMTP.
- Security matter for SMTP is worse.
- Transmission of binary files using SMTP is not possible without converting it into text files. Use MIME to send mail in another format.
- It is usefulness is limited by its simplicity.
- It is limited to only 7 bit ASCII characters.
- SMTP servers may reject all mail messages beyond some specific length.
- Usually require more back and worth conversion between servers in order to deliver your message, Which can delay sending and also increase the chance of the message not being delivered.
Requirements
All The Things You Need For Smtp Configuration
.
Host Address
Server host address is required to authenticate users or tools for sending outgoing messages using your email address.
Port Number
A port number is a way to identify a specific process to which the Internet or other network message is to be forwarded when it arrives at
a server.
Email Encryption
Email encryption is encryption of email messages to protect the content from being read by other entities than the intended recipients.
Popular SMTP Configurations
Email Clients And Their Smtp Settings
.

Airmail SMTP Settings

Aol Mail SMTP Settings

AT&T Webmail SMTP Settings

Gmail SMTP Settings

GMX Mail SMTP Settings

Hushmail SMTP Settings

iCloud SMTP Settings

Inbox by Gmail SMTP Settings

Lycos SMTP Settings

Mail.com SMTP Settings

Office 365 SMTP Settings

Outlook SMTP Settings

Rediffmail SMTP Settings

Verizon Webmail SMTP Settings

Yahoo Plus SMTP Settings

Yahoo SMTP Settings

Yandex Mail SMTP Settings

Zoho SMTP Settings
Send and Track Unlimited Emails with any Email Provider
Port Numbers And Their History
In computer networking, a port is a communication endpoint. At the software level, within an operating system, a port is a logical construct that identifies a specific process or a type of network service. A port is identified for each transport protocol and address combination by a 16-bit unsigned number, known as the port number. The most common transport protocols that use port numbers are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
And there are four major port numbers that identify SMTP process. They are 25, 465, 587 and 2525.
.
Port Number 25
SMTP port 25 is still mostly used in SMTP relaying. SMTP relaying refers to the transmission of email from an email server to the email server.
In most cases, modern SMTP email clients (Microsoft Outlook, Mail, Thunderbird, etc.) should not utilize this port. It is typically shut down by local ISPs as well as Cloud Hosting Providers in order to limit the volume of spam transferred through compromised servers or computers. If you’re not specifically managing the mail server, you should see no activity through that port in your server or computer.
Port Number 465
Port 465 was initially assigned to SMTPS (SMTP over SSL). After a brief time in this role the port was assigned to a different purpose and was deprecated.
In spite of that there are several ISPs as well as cloud-hosted providers continue to use port 465 to support SMTP submission.
Port Number 587
Port 587 serves as the standard port for SMTP upload on the internet of today. Although you may make use of other ports to submit (more on them later) but you should begin using port 587 as the default port and only switch to an alternative port if the circumstances demand (like your hosting provider blocking port 587 for reasons).
Port 587 also is compatible with TLS This means that you can send secure mail.
Port Number 2525
The port isn’t recognized by the IETF or IANA. Instead, Mailgun offers it as an alternative port that mirrors port 587 in the event that these ports have been blocked. Since 2525 isn’t a typical port number, it’s usually accepted by consumer ISPs as well as Cloud Hosting providers, such as Google Compute Engine. If you’ve tried the previous ports but are experiencing problems with connectivity, try port 2525. The port is also compatible with TLS encryption.
Encryption And Its Significance
SSL
TLS
It is important to note that TLS (Transport Layer Security) is simply an updated, and more secure variant of SSL. The term “security certificates” is used to refer to them as SSL because it’s an increasingly used term, however, when purchasing SSL at DigiCert you’re actually purchasing the most current TLS certificates, with the choice for the ECC option, RSA and DSA security.
The TLS protocol comprises two layers: the TLS record protocol and the TLS handshake protocol.
TLS Handshake Protocol
TLS is an encryption protocol designed to secure Internet communications. A TLS handshake is the process that kicks off a communication session that uses TLS encryption. During a TLS handshake, the two communicating sides exchange messages to acknowledge each other, verify each other, establish the encryption algorithms they will use, and agree on session keys. TLS handshakes are a foundational part of how HTTPS works.
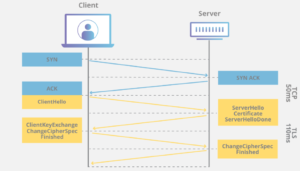
A TLS handshake happens when the user visits the website via HTTPS, and the browser then starts to request information from the origin server of the website. A TLS handshake is also triggered when any other communication uses HTTPS, which includes DNS calls as well as API calls. HTTPS requests.
TLS handshakes happen following the TCP connection was established through the TCP handshake.
TLS Record Protocol
The TLS Record Protocol is a multi-layered protocol. In each layer, messages can contain fields for description, length as well as content. Record Protocol Record Protocol takes messages to be sent, breaks messages into manageable chunks The data can be compressed then utilizes an MAC encryption, then transmits the results. The data received is decrypted, checked, decompressed and then reassembled before being delivered to clients with higher levels of security.
Quick Links
C4PLeadApp™ Vs Competitors
All Rights Reserved - ©2025 C4PLeadApp™

